Table of Contents
On the shelves of supermarkets, specialty shops but also in our offer, you will find many kinds of nuts. Let it be walnuts, almonds, cashews, pecans, para nuts, pine nuts, pistachios or hazelnuts. Although they offer almost identical health benefits and vitamins to the human body, each of these nuts is somehow specific. Therefore, we looked at some of the nuts, compared their positive and negative effects, and we would like to inform you about them in the following article.
1. ALMONDS
Almond is also called queen of nuts due to its properties and all the positive effects it offers to the human body. It is the fruit of the almond fruit tree and in Sweden they have a similar meaning during Christmas holidays as mistletoe in some countries. We know sweet and bitter almonds: there is no need to explain why sweet almonds are mostly used in gastronomy. The bitter ones have found application especially in medicine as a component of medicines against asthma, cough or bronchitis. Almonds high levels of potassium, magnesium and vitamin E. [1] [2]
Composition and nutritional values of almonds
30 g quantity contains [3]:
- calories: 163
- carbohydrates: 6 g
- dietary fibre: 3.5 g
- fats: 15 g
- protein: 6 g
- vitamin E: 50%
- vitamin B2: 22%
- copper: 31%
- magnesium: 18%
- manganese: 28%
The benefits almonds and their impact on health
- rich vitamin E content promotes healthy aging and prevents Alzheimer’s disease [1]
- magnesium reduces the pressure exerted on the blood vessels while promoting a healthy flow of oxygen and free radicals that act as oxidants in the body – damaging body cells and causing them to age [1]
- magnesium contained in almonds also reduces heart damage [1]
- flavonoids in cooperation with vitamin C and E have antioxidant effects [1]
- already in 1/4 cup there is a large amount of protein and dietary fibre that have a positive effect on your digestive system [1]
Who are almonds not suitable for?
Almonds contain a rich number of oxalates. These can cause kidney and gall bladder problems and interfere with the absorption of calcium into the body. Therefore, those with severe kidney problems should limit their intake of almonds. [1]
How to eat almonds?
You can do it the classic way, but if you’re not a fan of crunchy goodies, try ground almonds. Almond butter can be spread on toast, bread or mixed into sweet snack recipes. Playful Swedes diversified the consumption of almonds by hiding one almond in a rice pudding. According to tradition, the lucky man who found it in his serving should get married the following year. [1]

You might be interested in these products:
2. CASHEW NUTS
We can be grateful for the expansion of these nuts to Portuguese seafarers. They imported cashew nuts from Brazil to Mozambique and India. Later on, they spread it to Asia and far Africa. Few know that cashews are actually the fruit of a tree. They grow at the end of the cashew apples, which is the fruit of Anacardium occidentale. The apple is rich in vitamin C and has a sour taste. It is common to eat them only in some parts of the world – Africa or Brazil, for example. The shell of cashews includes irritating resins and acid and therefore, cashew nuts are already pre-peeled on sale. Aggressive substances from shells are used, for example, at wood varnish production. [4]
Composition and nutritional values of walnuts:
30 g of cashews contains [3]:
- energy value: 733 kJ
- calories: 175 kcal
- protein: 5.24 g
- carbohydrates: 7,79 g
- fats: 13.67 g
- dietary fibre: 0.63 g
- water: 1.3 g
- calcium: 9,75 mg
The effects of cashew on health
- they reduce the risk of gallstones and help fight bad LDL cholesterol [5]
- minerals and fatty acids richly represented in cashews promote weight loss. Cashew nuts contain a large amount of fats that enrich the satiety of foods [4]
- according to scientific knowledge, consumption of cashew nuts at least twice a week significantly reduces the risk of increased body weight [6]
- cashew nuts contain antioxidants that reduce the risk of liver and colon cancer on regular consumption [7]
- high levels of calcium, magnesium and potassium prevent bone demineralization. 1/4 cup of cashew provides more than 12% of the recommended daily dose of vitamin K, which protects bones from fractures or osteoporosis [4]
Who are cashews not suitable for?
In some cases, allergic reactions, especially in young children, may occur after eating cashew nuts. The cause is anacardic acid. Symptoms of allergic reactions to cashews are urticaria (light itchy skin), difficulty breathing, abdominal pain, vomiting or diarrhoea. [8]
How to eat cashew nuts?
Eating cashews can be a healthy substitute for fast food. Because the cashews are rich in fat, they fill hungry stomach and silence strange abdominal sounds efficiently and quickly. If you get tired of eating cashews over time, try cashew butter. Cashews spread on any type of bread can be consumed in the morning, evening, or as a snack. You can even use it as part of your protein drinks or as an ingredient for various sweet and savoury recipes. It’s only up to you what way you use the cashew butter in your kitchen.

3. WALNUTS
Walnuts are the most widespread nuts in our country that grow in every garden.Their original home are areas near the Mediterranean Sea and Central Asia. They are characterized by a hard shell that protects them from the weather pitfalls. Walnuts are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, besides containing a large number of antioxidants. They positively affect brain function and prevent heart disease or cancer. [9]
Composition and nutritional values of walnuts:
20 g of walnuts (a small handful of walnuts) contains [3]:
- energy value: 579 kJ
- calories: 138 kcal
- protein: 3.15 g
- carbohydrates: 2.89 g
- fats: 12.68 g
- dietary fibre: 1.185 g
- water: 0.8 g
- calcium: 19.13 mg
Benefits of walnuts and their impact on health
- walnuts are a very nutritional food supplement because of their high fat and protein content [3]
- their consumption ensures the intake of certain vitamins (E, B1, B6, B9) and minerals such as magnesium, copper or zinc, which have antioxidant effects and ensure proper functioning of the cells [1]
- nutrients contained in walnuts have a positive effect on the human psyche, sexual potential, hair, nails and skin [3]
- rich levels of omega-3 fatty acids regulate blood pressure and prevent cardiovascular disease [3]
- 1/4 cup of these nuts corresponds to 90% of the recommended daily dose of omega-3 [3]
- walnuts improve endothelial function. Endothelial lining damage (endothelial dysfunction) is the origin of vascular changes that can result in atherothrombotic complications [10] [11]
- they reduce cholesterol and improve lipid profile. A series of examinations that make up the lipid profile have been shown to be a good indicator of the risk of heart attack or stroke [12] [13]
Who are walnuts not suitable for?
Although walnuts are very healthy, be careful about what amount of them you eat. Nuts are fatty and a large dose of eaten nuts can cause stomach pain. In some people, phytic acid (found in all nuts) may cause decreased absorption of minerals. [3] [14]
How to eat walnuts?
They can be eaten in raw state, but you can also eat walnuts as part of salads, pasta, cereals, soups or bread. They are also used for the production of nut oil. Oil made of walnuts finds its application in the kitchen (for salads, confectionery and toppings), but also in cosmetics (massage oil, part of creams and hair products). Peeled walnuts last fresh for 4 to 6 months, frozen nuts are recommended to be stored for up to one year in the freezer. [15] [3]

4. PECAN NUTS
Some Indian tribes in Central and South America used pecans as their main food source. In addition to their consumption, they also served as a cure for skin and lung diseases. The pecan has a shape similar to walnut, but it tastes a little sweeter. Unlike walnuts, pecans contain more fat and less omega-3 fatty acids. [2]
Composition and nutritional values of pecans
20 g of pecans (handful of pecans) contains [3]:
- energy value: 612.63 kJ
- calories: 146.42 kcal
- protein: 1.84 g
- carbohydrates: 2.77 g
- fats: 14,208 g
- dietary fibre: 1.92 g
- water: 0.722 g
- calcium: 13.1 mg
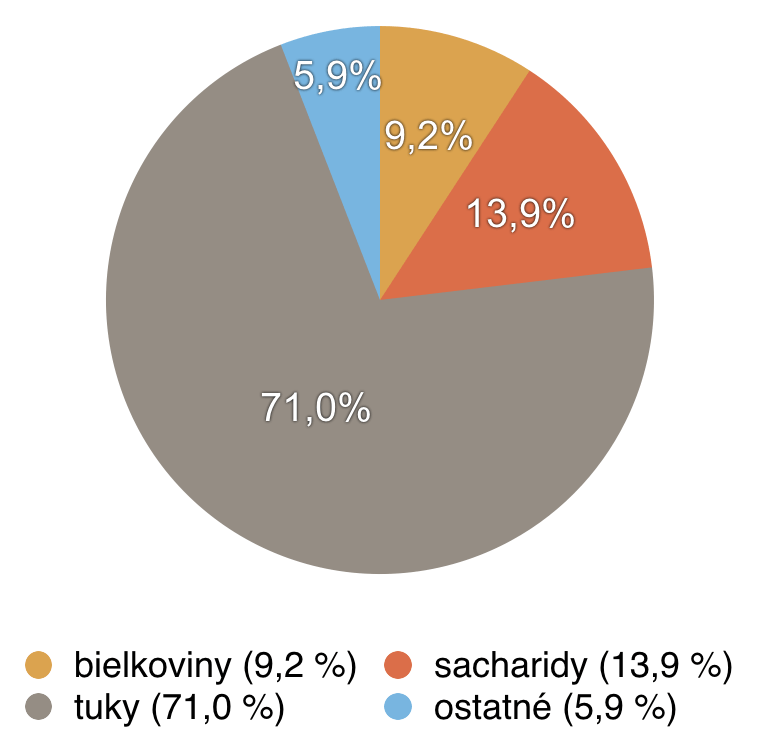
Benefits of pecans and their impact on health
- pecans increase antioxidant capacity, reduce bad LDL and increase good HDL cholesterol [16] [17]
- inclusion of pecans in the diet improves lipid profile [17]
- rich fibre supports healthy digestive tract and reduces the risk of haemorrhoids and colon cancer [18]
- oleic acid and phenoplastic antioxidants help prevent stroke and ischemic heart disease due to insufficient blood flow [19]
- consumption of magnesium-rich pecans (125, 5 mg in 20 g) reduces blood pressure. 100 mg of magnesium a day reduces the risk of stroke by up to 9% [20] [3]
- the presence of magnesium has anti-inflammatory effects, for example in the arterial wall, reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease, arthritis and Alzheimer’s disease [21]
Who are pecans not suitable for?
In some cases, allergic reactions, especially in young children, may occur after eating pecans. The cause is anacardic acid. Symptoms of an allergic reaction to pecans are urticaria (light itching of the skin), difficulty breathing, abdominal pain, vomiting or diarrhoea. [8]
How to eat pecans?
They can be eaten raw, ground, grated or in a form of nut puree. As part of appetizers, soups, salads or sweet desserts. The use of pecans in the kitchen is similar to the use of walnuts. They can be part of every healthy diet, but they can be also included in the menu of people who have decided to try a reduction diet. [1] [3]

5. PINE NUTS
In fact, pine nuts are not. These are the seeds of Mediterranean pinecones. Like many nuts, they also contain this alpha-linolenic acid (omega-3) beneficial for the heart and vitamin B. In contrast to the previous types of nuts pine nuts are also characterized by high protein. [1]
Composition and nutritional values of pine nuts
20 g of pine nuts contains [3]:
- energy value: 509.93 kJ
- calories: 121.87 kcal
- protein: 4.80 g
- carbohydrates: 2.944 g
- fats: 10.14 g
- dietary fibre: 0.90 g
- water: 1,338 g
- calcium: 5.2 mg
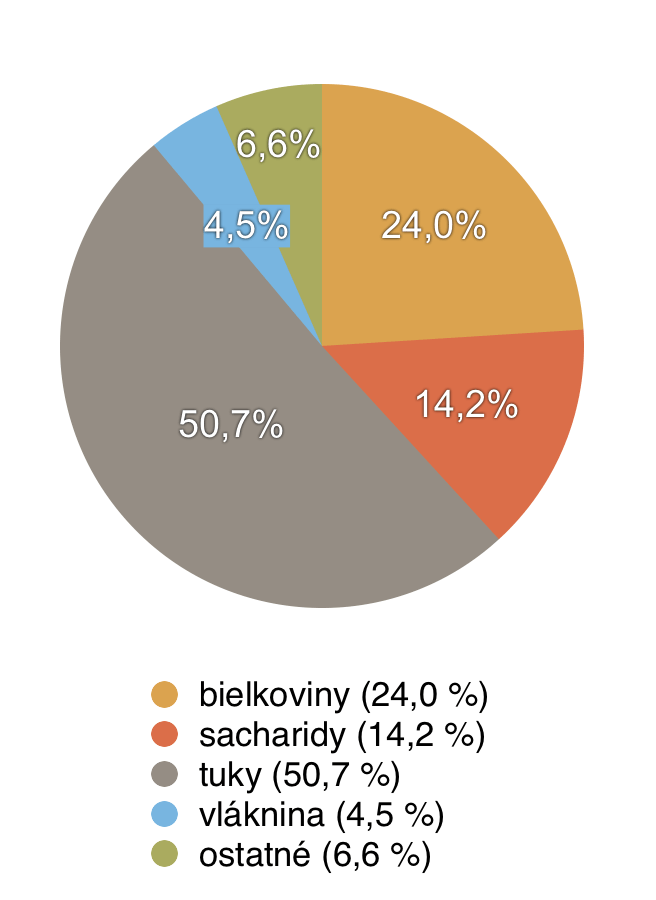
Benefits of pine nuts and their impact on health
- pine cedar nuts containing cholecystokinin (CCK hormone) suppress appetite [22] [23]
- 1/2 cup of pine nuts provides almost 50% of the recommended daily amount of magnesium [24]
- monounsaturated fatty acids such as magnesium, vitamin E, vitamin K and manganese promote healthy heart function [24]
- pinolenic acid found in pine nuts maintains optimal cholesterol levels and reduces harmful LDL cholesterol [25]
- content of antioxidants and vitamins A, B, C, D and E protect cells from reactive oxygen radicals (ROS) [24]
- lutein is a substance that can heal various eye diseases, such as macular degeneration (loss of central vision) [24]
Who are pine nuts not suitable for?
In some, pine nuts may cause a bitter taste in the mouth. These are rare cases that cannot be predicted and can also occur in people who have consumed pine nuts in the past without any consequences. [26]
How to eat pine nuts?
As they contain large amounts of fat, peeled pine nuts are prone to yellowing. To prolong the freshness of nuts, it is recommended to store them in a refrigerator. They can be eaten raw, roasted or as part of vegetable salads. They have a very wide application in the production of pesto. To make a simple pesto sauce, all you need is fresh basil, olive oil, parmesan and pine nuts. [1] [24]

6. PISTACHIOS
Already in the Old Testament, pistachios along with honey, almonds and myrrh were marked as the best that Egypt could offer the world. Pistachios have many of the same effects on the heart as other nuts, but because they contain more antioxidants, such as lutein and zeaxanthin, they also prevent eye diseases and eye damage. They are an excellent source of fibre, vitamin B6, magnesium and calcium. [1] [2]
Composition and nutritional values of pistachios
20 g of pistachios contains [3]:
- energy value: 523.75 kJ
- calories: 125.18 kcal
- protein: 3,948 g
- carbohydrates: 5.074 g
- fats: 9.896 g
- dietary fibre: 1.507 g
- water: 0.942 g
- calcium 26 mg
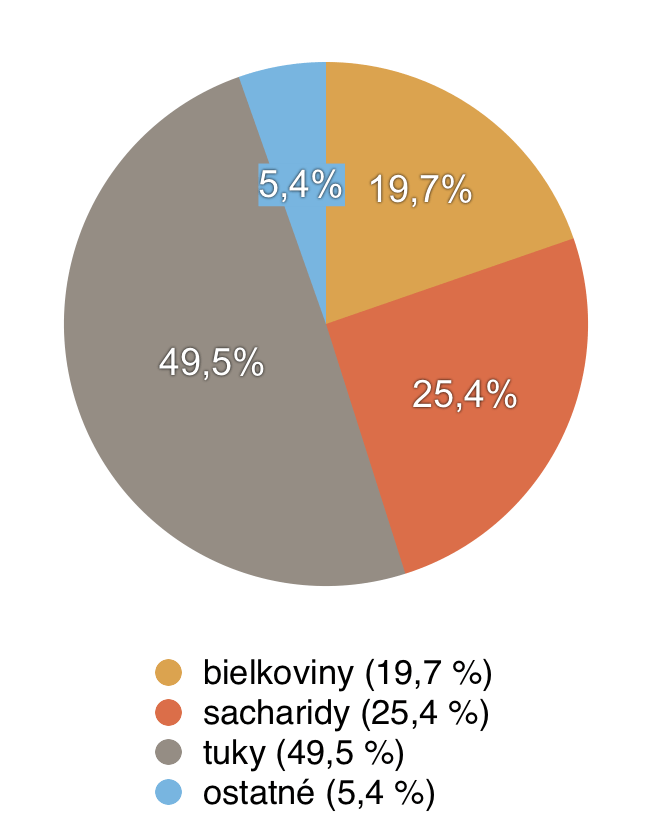
Benefits of pistachios and their impact on health
- high phytosterol content lowers both total and dangerous LDL cholesterol [1]
- probiotic fibre has beneficial effects on the intestinal microflora, even more than almonds [27]
- pistachios lower blood pressure [3]
- reduce postprandial blood glucose [22]
- improve metabolic syndrome [29]
Who are pistachios not suitable for?
In some cases, allergic reactions, especially in young children, may occur after consumption of pistachios. The cause is anacardic acid. Symptoms of an allergic reaction to pistachios include urticaria (light itchy skin), difficulty breathing, abdominal pain, vomiting or diarrhea. [8]
How to eat pistachios?
In the raw state, when they contain the most nutrients. Or try combining vegetables, rice or pasta with pistachio sauce. You will need 750 ml of soymilk, salt and pepper to make it. Bring this mixture to the boil and slowly add the finely ground pistachios. The sauce is ready when the mixture gets thick. [1]

7. HAZELNUTS
Hazelnuts are an excellent dietary supplement for diabetics. They promote healthy brain function, reduce the risk of prostate cancer, and increase stress resistance. The archaeological fossils from prehistoric times determined the Asian origin of the hazelnuts. People most often know hazelnuts as part of Nutella, who, admittedly, has little to do with healthy eating. Already 30 grams of hazelnuts provide 9% of total daily energy intake. [1] [3] [30] [31]
Composition and nutritional values of hazelnuts
20 g of hazelnuts contains [3]:
- energy value: 572.02 kJ
- calories: 136.71 kcal
- protein: 2.92 g
- carbohydrates: 3.15 g
- fats: 12.484 g
- dietary fibre: 1,745 g
- water: 1.032 g
- calcium: 36,192 mg
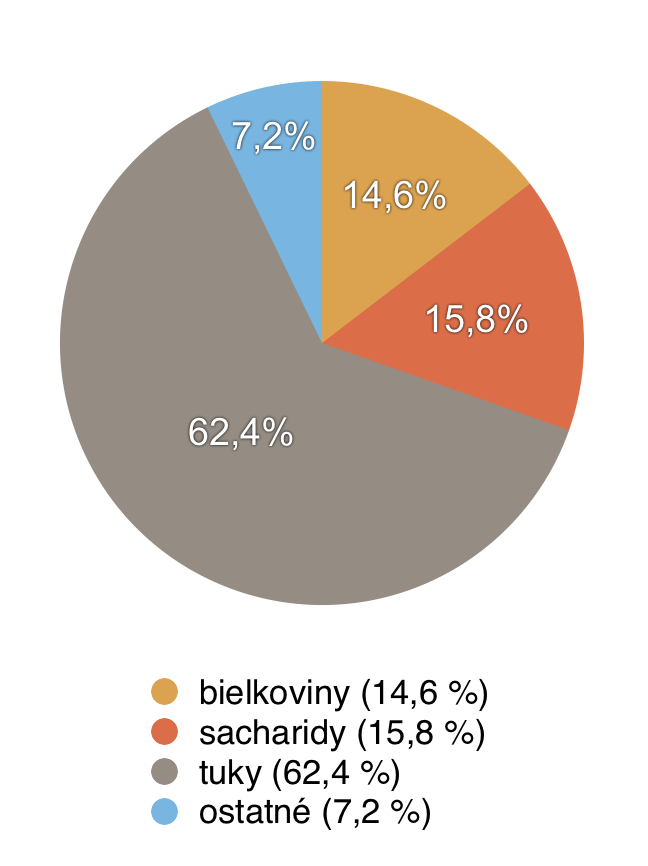
Benefits of hazelnuts and their impact on health
- along with Brazil (para) nuts, hazelnuts are an excellent source of calcium that is beneficial for strong bones and healthy teeth [1]
- they contain beneficial monounsaturated fats [1]
- have a preventive function against prostate cancer while increasing resistance to stress [3]
- hazelnuts are among the richest sources of polyphenol compounds. The value of polyphenols in hazelnuts is 7 to 8 times higher than in dark chocolate, 10 times higher than in coffee and up to 25 times higher than that of blackberries. Polyphenols have antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, antimutagenic, antiphlogistic and antidiabetic properties [32] [33]
- high fibre content of hazelnuts reduces LDL cholesterol oxidation and improves blood lipids [34]
Who are hazelnuts not suitable for?
Because of their high fat content, it is recommended to consume hazelnuts in smaller doses. In addition, hazelnuts contain moderately high amounts of phytates that preserve and protect nutrients. An adverse effect of phytates is the possible interaction with digestive enzymes that cannot decompose phytate-containing food. [3] [35] [36]
How to eat hazelnuts?
In addition to the raw state, you can consume hazelnuts roasted, as a paste or as an ingredient in healthy foods. If you don’t mind the increased sugar content, try hazelnut spreads and butters. There is also hazelnut oil produced, which is widely used in the kitchen. For example, as a salad dressing. [3]

8. PARA NUTS (BRAZIL NUTS)
Brazil nuts have been part of the diet of indigenous Amazon tribes for centuries. They are characterized by a high content of selenium, which in addition to the antioxidant function prevents cirrhosis of the liver, lung, breast and liver cancer. To avoid these diseases, just eat 2 para nuts a day. [2]
Composition and nutritional values of Brazil nuts
10 g of para nuts (small portion) contains [3]:
- energy value: 294.97 kJ
- calories: 70.5 kcal
- protein: 1,429 g
- carbohydrates: 1.052 g
- fats: 6.725 g
- dietary fibre: 0.585 g
- water: 0.418 g
- calcium: 16 mg
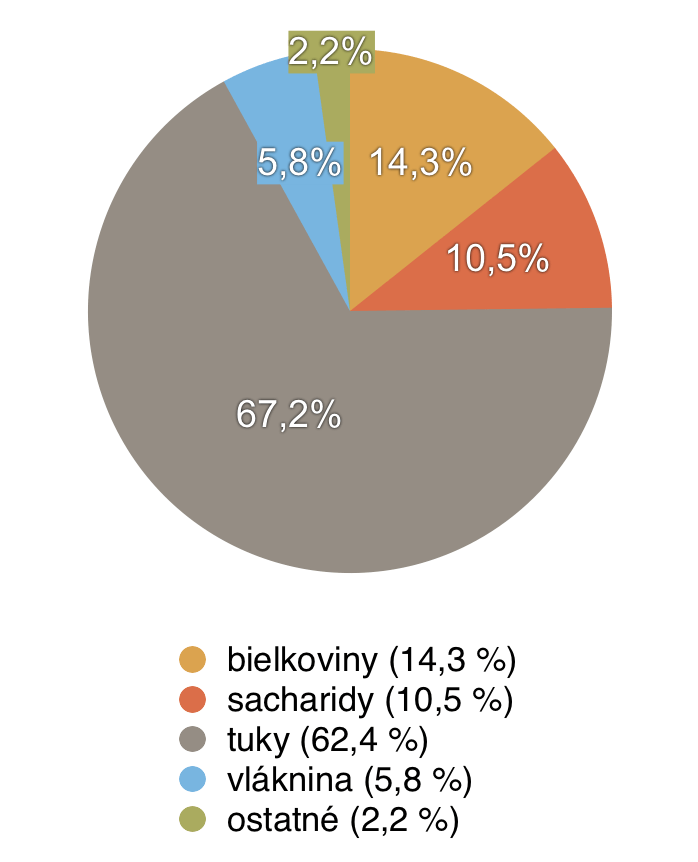
Benefits of Brazil nuts and their impact on health
- rich selenium content ensures smooth thyroid gland, has antioxidant effects, fulfils immune function, protects against cardiovascular diseases and cancer. All you need to do is to consume only 2 Brazil nuts per day (500 g Brazil nuts from our offer will last for up to 1/4 year) [2] [35]
- one serving of Brazil nuts improves lipid profile. A series of examinations that make up the lipid profile have been shown to be a good indicator of the risk of heart attack or stroke [13] [37]
- Brazilian nuts affect inflammation retreat [38]
- they relieve stress and irritability, making Brazil nuts a perfect substitute for cigarettes in people who try to stop smoking [3]
- selenium in Brazil nuts acts as a catalyst for thyroid hormones [39]
- selenium in Brazil nuts also reduces the risk of oesophageal cancer [40]
Who are not Brazilian nuts suitable for?
You do not have to worry about an overdose of selenium, its abundance does not have any negative effects and is not dangerous to health. As with all nuts, the rule applies – for high fat content, consume them in reasonable quantities. [41]
How to eat Brazil nuts?
Baked, salted, any but the best tastes raw, providing the human body with the most vitamins and health benefits. You can use crushed Brazil nuts as part of various desserts and puddings. Brazil milk is a great alternative to almond and soymilk. Peeled Brazil nuts do not have a long shelf life, so obtain them in reasonable quantities and in hermetically sealed packages. Don’t eat suspiciously looking Brazilian nuts with a bitter taste and white colour, but rather throw them to the bin. In airtight containers, in a dark, dry place (eg in a refrigerator), Brazil nuts will last for several months.

[1] Quan, S.B., D. Everything You Need to Know About Nuts – https://www.canadianliving.com/health/nutrition/article/everything-you-need-to-know-about-nuts
[2] Milner, C. All About Nuts. 2015 – https://www.theepochtimes.com/n3/1143397-all-about-nuts/
[3] Kalorické tabulky – Ořechy a semena – https://www.kaloricketabulky.cz/pochoutky/orechy-a-semena/
[4] Axe, J. Cashews Nutrition: Helps Prevent Cancer, Diabetes & More – https://draxe.com/nutrition/cashews-nutrition/
[5] Ros, E. Health Benefits of Nut Consumption – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257681/
[6] Bes-Rastrollo, M. Nut consumption and weight gain in a Mediterranean cohort. 2007. University of Navarra : Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17228038
[7] Bao, Y. Nut consumption and risk of pancreatic cancer in women. 2013. British Journal of Cancer – https://www.nature.com/bjc/journal/v109/n11/full/bjc2013665a.html
[8] Nutrition and You. Cashew nut nutrition facts – https://www.nutrition-and-you.com/cashew_nut.html
[9] Hayes, D., Angove, M., J., Tucci, J., Dennis, C. Walnuts (Juglans regia) Chemical Composition and Research in Human Health. 2015 – https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10408398.2012.760516
[10] Katz, D., L., Davidhi, A., Ma ,Y., Kavak, Y., Bifulco, L., Njike, VY. Effects of walnuts on endothelial function in overweight adults with visceral obesity: a randomized, controlled, crossover trial. 2012 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3756625/
[11] Vrablík, M., Janotová, M., Motyková, E., Prusíková, E. Endoteliální dysfunkce – první stadium aterosklerózy. 2011. Medicína pro praxi 2011/8 – https://www.medicinapropraxi.cz/pdfs/med/2011/03/05.pdf
[12] Etherton, K., P.,M. Walnuts Decrease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Summary of Efficacy and Biologic Mechanisms. 2014
[13] LabTestsOnline. Lipidový profil – https://www.labtestsonline.cz/lipidovy-profil.html
[14] Macfarlane, B., J. Inhibitory effect of nuts on iron absorption. 1988 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3341259
[15] Arnarson, A. Walnuts 101: Nutrition Facts and Health Benefits – https://authoritynutrition.com/foods/walnuts/
[16] Hudthagoso, Ch., Haddad, E.,H., McCarthy, K., Wang, P., Oda, K., Sabaté, J. Pecans Acutely Increase Plasma Postprandial Antioxidant Capacity and Catechins and Decrease LDL Oxidation in Humans. 2011
[17] Rajaram, S., Burke, K., Connell, B., Myint, T., Sabaté, J. A Monounsaturated Fatty Acid–Rich Pecan-Enriched Diet Favorably Alters the Serum Lipid Profile of Healthy Men and Women. 2001
[18] World's Healthiest Foods. Fiber – https://www.whfoods.com/genpage.php?tname=nutrient&dbid=59
[19] Haddad, E., Jambazian, P., Karunia, M., Tanzman, J., Sabaté, J. A pecan-enriched diet increases γ-tocopherol/cholesterol and decreases thiobarbituric acid reactive substances in plasma of adults. 2006 – http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.511.13&rep=rep1&type=pdf
[20] Larsson, C., S., Orsini, N., Wolk, A. Dietary magnesium intake and risk of stroke: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. 2012
[21] Chacko, S.,A., Song, Y., Nathan, L., Tinker, L., de Boer, I.,H., Tylavsky, F., Wallace, R., Liu, S. Relations of Dietary Magnesium Intake to Biomarkers of Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction in an Ethnically Diverse Cohort of Postmenopausal Women. 2009 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2809271/
[22] Pasman, W., J., et al. The effect of Korean pine nut oil on in vitro CCK release, on appetite sensations and on gut hormones in post-menopausal overweight women. 2008 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2322999/
[23] Einerhand, A., W. Korean pine nut fatty acids affect appetite sensations, plasma CCK and GLP1 in overweight subjects. 2006 – https://www.fasebj.org/cgi/content/meeting_abstract/20/5/A829-c
[24] Mercola. Pine Nut Benefits: 5 Ways This Nutritious Seed Can Rejuvenate Your Body. 2015 – https://articles.mercola.com/sites/articles/archive/2015/01/19/pine-nuts-benefits.aspx
[25] Lee, J., W. Selective increase in pinolenic acid (all-cis-5,9,12-18:3) in Korean pine nut oil by crystallization and its effect on LDL-receptor activity. 2004 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15357026
[26] Abcarian, R. Ever heard of 'pine nut syndrome'? Neither had I, until I got it. 2014 – https://www.latimes.com/local/abcarian/la-me-ra-bad-taste-in-my-mouth--20140722-column.html
[27] Ukhanova, M., Wang, X., Baer, D., J., Novotny, J.A., Fredborg, M., Mai, V. Effects of almond and pistachio consumption on gut microbiota composition in a randomised cross-over human feeding study. 2014 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24642201
[28] Kendall, C., W., a kol. Acute effects of pistachio consumption on glucose and insulin, satiety hormones and endothelial function in the metabolic syndrome. 2014 – https://www.nature.com/ejcn/journal/v68/n3/full/ejcn2013275a.html
[29] Holligan, S., D., a kol. A moderate-fat diet containing pistachios improves emerging markers of cardiometabolic syndrome in healthy adults with elevated LDL levels. 2014 – https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition/article/a-moderate-fat-diet-containing-pistachios-improves-emerging-markers-of-cardiometabolic-syndrome-in-healthy-adults-with-elevated-ldl-levels/C2A0A70A1431D9A5D0EFB23A4460365B
[30] Axe, J. Hazelnuts: 7 Benefits of These Heart-Healthy, Brain-Boosting Nuts – https://draxe.com/nutrition/hazelnuts/
[31] Andrews, J. What Are the Health Benefits of Hazelnuts? 2015 – https://www.livestrong.com/article/287534-what-are-the-health-benefits-of-hazelnuts/
[32] Calani, L., a kol. Colonic Metabolism of Polyphenols From Coffee, Green Tea, and Hazelnut Skins. 2012 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22955368
[33] Süli, J., Homzová, K. Sobeková, A., Bujdošová, Z., Hrušková, T. Polyfenolové látky v potravinách. 2014 – https://docplayer.net/41031804-Polyfenolove-latky-v-potravinach.html
[34] Yücesan, F., B., Orem, A., Kural, B., V., Orem, C., Turan, I. Hazelnut consumption decreases the susceptibility of LDL to oxidation, plasma oxidized LDL level and increases the ratio of large/small LDL in normolipidemic healthy subjects. 2010 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20150001
[35] Sisson, M. The Definitive Guide to Nuts. 2015 – https://www.marksdailyapple.com/the-definitive-guide-to-nuts
[36] Paleo.sk. Problematické látky v potrave – fyláty – http://www.paleo.sk/preview-file/e5e589e570a4a2c98c8827881e5f83a7
[37] Colpo, E., a kol. A Single Consumption of High Amounts of the Brazil Nuts Improves Lipid Profile of Healthy Volunteers. 2013 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3693158/
[38] Colpo, E., a kol. Brazilian nut consumption by healthy volunteers improves inflammatory parameters. 2014 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24607303
[39] Rayman, M., P. The importance of selenium to human health. 2000 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10963212
[40] Mark, S.,D. a kol. Prospective study of serum selenium levels and incident esophageal and gastric cancers. 2000 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11058618
[41] Lemire, M., a kol. No evidence of selenosis from a selenium-rich diet in the Brazilian Amazon. 2012 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21856002
